Major IT Disciplines and Specializations.
Major IT Disciplines and Specializations.
Introduction to IT Disciplines and Specializations:

Major IT Disciplines and Specializations. Information technology (IT) is a crucial component of almost every area of our life in the modern digital era. It has a significant impact on how modern society is shaped, influencing everything from communication and entertainment to company operations and scientific research. This introduction offers a glimpse into the fascinating specializations that professionals might pursue as well as the varied universe of IT disciplines.
Exploring IT Disciplines and Specializations
In our digital era, Information Technology (IT) permeates every facet of life, making understanding its diverse disciplines and specializations crucial.
Defining IT Diversity:
It encompasses various focused domains, including Software Development, Data Science, Network Security, Information Systems Management, UI/UX Design, Cloud Computing, and Emerging Technologies.
Integral Role:
IT powers modern society, driving businesses, healthcare, education, and research, making its different facets indispensable.
Choosing Your Path:
IT professionals have an array of options. Data enthusiasts might delve into Data Science, while creatives could excel in UI/UX Design. Security-minded individuals can explore Cybersecurity, and tech enthusiasts may embrace Emerging Technologies.
Impact and Innovation:
As technology evolves, IT remains at the forefront of progress, offering numerous opportunities for individuals to contribute their skills and shape our digital future.
Software Development and Engineering:

Software Development and Engineering stand as the cornerstone of the Information Technology (IT) landscape, driving innovation, efficiency, and functionality across various sectors. This discipline revolves around crafting and maintaining software solutions that cater to diverse needs, from entertainment and communication apps to complex enterprise systems.
Key Elements:
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC):
A structured approach encompassing stages like planning, designing, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance, ensuring high-quality software products.
Application Types:
Software Development spans web applications, mobile apps, desktop software, and even embedded systems that power devices like smart appliances and vehicles.
DevOps Practices:
DevOps integrates development and IT operations to enable continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and rapid deployment, enhancing collaboration and efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions:
Complexity:
Developing software that meets intricate requirements while maintaining usability and performance demands expertise and careful planning.
Changing Requirements:
Adapting to evolving user needs and market trends requires agile development methodologies that prioritize flexibility.
Security Concerns:
Addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring data privacy is critical, making secure coding practices and regular audits essential.
Data Science and Analytics:
In the era of information overload, Data Science and Analytics emerge as the guiding light, extracting invaluable insights from vast datasets. This multidisciplinary field incorporates advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain expertise to make educated decisions and signify trends.
Key Components:
Data Collection and Preparation:
Collecting data from various sources, cleaning, and converting it into usable formats for research.
Statistical Analysis:
Using statistical techniques to uncover patterns, correlations, and trends within the data.
Machine Learning:
Utilizing algorithms to build predictive models that learn from data and make accurate forecasts.
Data Visualization:
Representing complex data findings through graphs, charts, and dashboards for easier comprehension.
Big Data Technologies:
Using tools like Hadoop and Spark to control huge datasets efficiently.
Role in Industries:
Business and Marketing:
Predicting consumer behavior, optimizing marketing strategies, and identifying market trends.
Healthcare:
Analyzing diseases, indicating patient results, and improving medical research.
Finance:
Catching dishonest activities, managing risks, and making investment forecasts.
E-commerce:
Suggesting products, personalizing user experiences, and optimizing cache chains.
Science and Research:
Analyzing experimental data, simulating scenarios, and accelerating scientific discovery.
Impact on Society:
Data Science and Analytics revolutionize industries by optimizing operations, improving efficiency, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
In nature, Data Science and Analytics function as modern-day alchemy, converting raw data into gold abundances of knowledge.
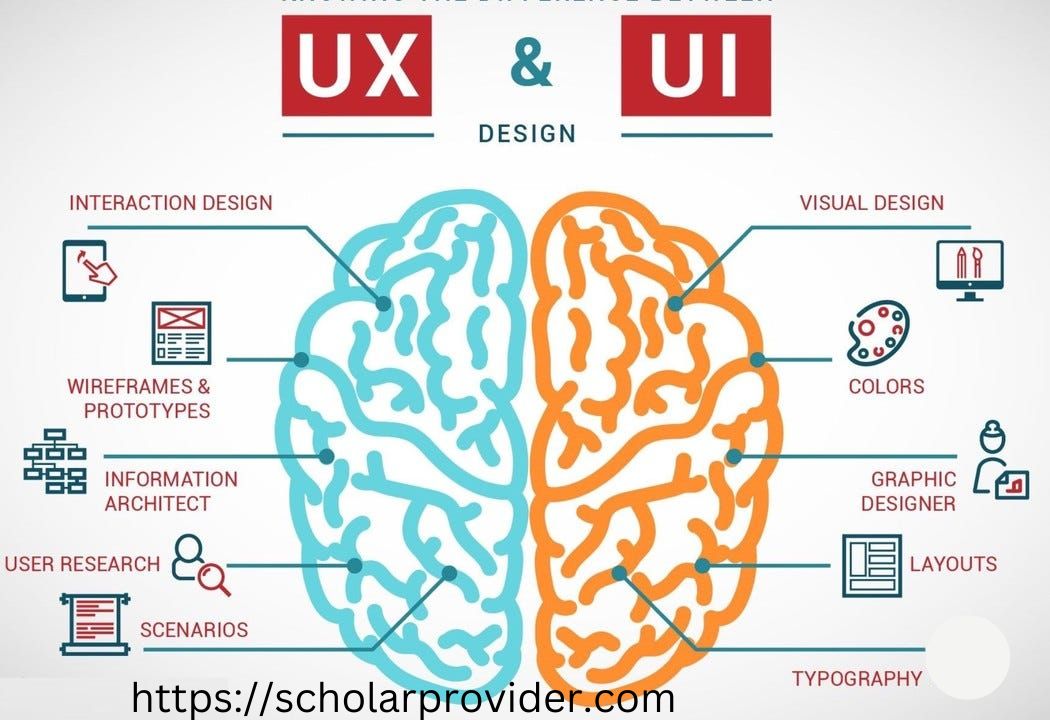
User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design are key fields in the domain of Information Technology, which seeks to create intuitive, attractive, and user-centric digital adventures. While closely related, UX and UI design serve different roles in shaping how users interact with digital products, yet affecting user happiness, retention, and overall business win.
User Experience (UX) Design:
Every touchpoint and element of a user’s journey is taken into account in UX design, which is concerned with the overall experience people have when interacting with a digital product. Making sure that the user’s needs, actions, and emotions are recognized and taken into account during the design process is the main objective of UX design. This entails:
User Research:
User research is the process of accomplishing in-depth analysis to understand user preferences, behaviors, pain spots, and motives.
User Personas:
Making fictitious characters to represent various user types might help designers better understand the demands of their target audience.
Information Architecture:
The method of organizing and managing content so that customers may interact with it with ease.
Wireframing and Prototyping:
Creating low-loyalty mockups (wireframes) and interactive prototypes to imagine the design and functionality of the product.
Usability Testing:
Testing the product’s usability with real consumers to spot problems and potential areas for development.
User Interface (UI) Design:
The goal of UI design is to make digital development visible and interactive components attractive to the eye, readable, and simple to use. Even though it is a subset of UX design, user interface (UI) design is crucial in establishing the user’s perception and directing their interactions. Key UI design components include:
Visual Design:
Preparing the general look and feel of the development, including color schemes, typography, icons, and imagery.
Layout and Composition:
Arranging elements on the screen in a balanced and logical manner, considering hierarchy and flow.
Interaction Design:
Organizing how users interact with features, including buttons, forms, navigation menus, and animations.
Responsive Design:
Ensuring the product works seamlessly across various devices and screen sizes.
Consistency:
Maintaining a uniform design language throughout the development to create a cohesive understanding.
See More: Pakistan Defeat Netherlands By 81 Runs
